Category: Depression
By Peter White, M.A., LPCC, LICDC, Lindner Center of HOPE Outpatient Therapist
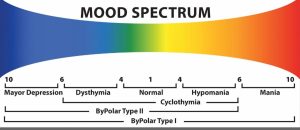
The problem during Bipolar Mood Disorders is a pattern of swings of the essential elements of mood between the two poles, like the North Pole and South Pole, of Mania and Depression. These swings are not moodiness, which are swings of mood throughout a day. A Bipolar swing is a distinct period of at least one week when the full spectrum of mood elements exhibits depressive and/or manic elements.
Although thought of as a subjective experience, mood deeply influences three areas. First is metabolism – sleep, appetite, libido and energy levels. Second, mood influences both motivation as well as the ability to experience pleasure and/or a sense of accomplishment. Thirdly, mood deeply influences interpretations within thoughts from positive to neutral to negative.
So, we can think of this first spectrum of mood disorder along an axis of depression to neutral to manic. Therefore, a depressed mood will depress metabolism. A person will have difficulty with sleep through either excessive or inadequate or disrupted sleep, loss of appetite or excessive eating despite disrupted appetite, loss of libido as well as loss of energy. Depression will hinder motivation making it difficult to experience the drive to initiate activities as well as hinder pleasure or the reward of activity. This is a very difficult cycle when it is hard to get active in the day compounded by not finding any pleasure or reward in the day’s activities. Lastly, depression will darken the flow of thoughts adding many themes of hopelessness, helplessness, worthlessness and guilt into our thought process.
Conversely, mania will elevate the same essentials. It will increase energy levels often in the face of declining sleep hours. It will increase libido, increase excessive and/or absence of appetite. It will increase motivation often leading to excessive engagement of plans or activities and will create a compounding loop of all activity feeling especially pleasurable or rewarding. Again, conversely is will paint thinking with elevated judgements of specialness, invulnerability, and inevitable positive outcomes.
The second spectrum of mood disorders, like most other behavioral health problems, is along the spectrum of severity – mild to moderate to severe. If you combine this spectrum of severity along with the first spectrum of depressive to manic, we see how varied and individualized any person’s experience with Bipolar Mood disorders can be. Most people can relate to some degree of depression during periods of their life with perhaps a few weeks or month of low energy, noticing that they are not getting the same rewards in their regular activity as well as perhaps noticing they are thinking unusually negatively about themselves and their outlook on life. We might call this a mild, brief depressive episode. But the reality is that depression is one of the most disruptive and costly of all health conditions as recognized by the World Health Organization. This mean that depression is often moderate or severe to very severe and can disrupt functioning on every level for weeks to months if not years. A severe depression can make it difficult to get out or bed for days on end both from collapsed energy and motivation. It can destroy the pleasure and rewards of living so that all activity feels like a painful chore at best. Finally, it can turn thoughts dangerously dark with so much hopelessness, helplessness and worthless that suicidal thinking emerges nearly with a sense of relief.
Again conversely, though experienced less often by most people, Manic Episodes can present with mild, moderate, severe and very severe intensity. During a sever episode, a person with manic symptoms is often sleeping little but maintaining very high levels of energy. They are often talking very quickly and sometimes laughing excessively and outside the context of humorous things. Given the very high levels of motivation and the reinforcement of pleasure in all activities, they often initiate an excessive number of activities – starting multiple projects with little awareness of the ability to balance or complete them. They frequently initiate conversations or relationship in an open or disinhibited style very unusual for to their character. With elevated thought patterns, they might believe they have a unique or special purpose, and they are convinced that all their activities will be successful and rewarding. Give the excessive energy, motivation, pleasure and elevated sense of self and success, people in manic states will often engage in behavior patterns much riskier than typical – spending money well beyond their mean, unusually disinhibited sexual decision, reckless driving, shop lifting.
I hope it’s useful to review the way mood symptoms fluctuate along these two spectrums, because like all health care conditions, we are best off when we accurately identify what these behaviors are – symptoms. Mood symptoms are not moral challenges, personality traits or unconsciously desired behaviors. Mood symptoms are symptoms, and fortunately, there are many very effective treatments for all symptoms along both spectrums. Please know if you or a loved one or a client is experiencing any degree of Bipolar mood problems, there will be many ways to help and cope, and experience the satisfaction of effectively treating a behavioral health care condition.